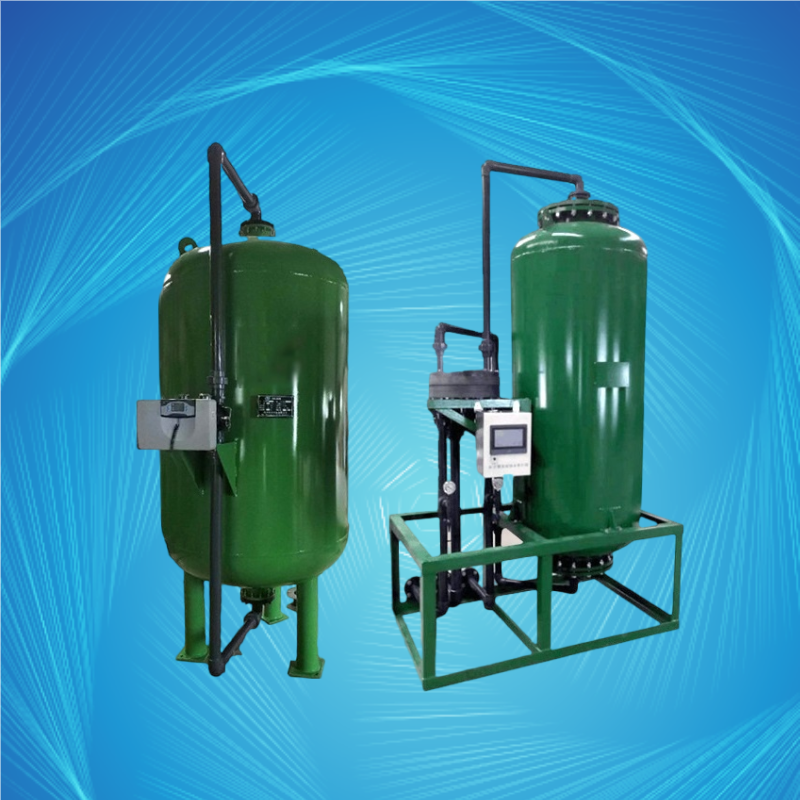
Activated Carbon Filter
1.Working Principle
Activated Carbon Filter is a commonly used water treatment equipment. As a pretreatment device for water desalination systems, it can adsorb residual chlorine that cannot be removed by previous-stage filtration, effectively prolonging the service life of subsequent equipment, improving water quality, and preventing pollution. Specifically, it prevents the contamination of free residual chlorine on subsequent reverse osmosis membranes, ion exchange resins, etc. What is the principle of the Activated Carbon Filter? Let's explore it below.
Activated carbon, a type of amorphous carbon, is composed of many microcrystals arranged irregularly in a layered structure resembling graphite. It has crystal defects, a huge specific surface area, and a porous structure. Classified by its raw materials, activated carbon can be divided into coal-based activated carbon, wood-based activated carbon, nutshell activated carbon, and bone activated carbon. By its shape, it can be categorized as columnar carbon, crushed carbon, powdered carbon, and fibrous activated carbon. The main raw materials for activated carbon are organic materials rich in carbon elements, such as coal, wood, nutshells, etc. Through activation, these materials form a complex porous structure with adsorption capacity. The pores with a radius greater than 20,000 nm are classified as macropores, those between 150 and 20,000 nm are mesopores, and those less than 150 nm are micropores. The adsorption effect of activated carbon mainly occurs in these voids and on its surface. The large number of molecules on the activated carbon pore walls can generate strong attraction to attract impurities in water and air into the pores.
The adsorption of activated carbon can be divided into physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. Physical adsorption mainly occurs in the abundant micropores of activated carbon and is used to remove impurities from water and air, with the molecular diameter of these impurities being smaller than the pore size of activated carbon. Different raw materials and processing techniques result in activated carbon with different micropore structures, specific surface areas, and pore sizes, suitable for different applications. Activated carbon not only contains carbon elements but also has functional groups on its surface that can react chemically with adsorbed substances, often occurring on the surface of activated carbon. Impurities in the medium continuously enter the porous structure of activated carbon through physical and chemical adsorption, causing saturation and a decrease in adsorption effectiveness. Saturated activated carbon requires reactivation and regeneration to restore its adsorption capacity for reuse. The main evaluation indicators for the adsorption performance of activated carbon include methylene blue value, iodine value, and caramel adsorption value. The larger the adsorption capacity, the better the adsorption effect.
2.Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of activated carbon involves two stages: dehydration and carbonization, followed by activation. This creates a unique porous structure, resulting in a huge surface area and strong physical adsorption capacity. Additionally, during the activation process, some oxygen-containing functional groups, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, and carbonyl groups, form on the non-resultant parts of the activated carbon surface, endowing it with chemical adsorption, catalytic oxidation, and reduction capabilities.
3.Applications
Activated Carbon Filters utilize the adsorption and decolorization capabilities of activated carbon to remove impurities from liquids, purifying them. Its adsorption and decolorization capabilities are primarily reflected in the following aspects:
1. Adsorption of organic matter, bacteria, colloidal particles, and microorganisms in water.
2. Adsorption of non-metallic substances such as chlorine, ammonia, bromine, and iodine.
3. Adsorption of metal ions, such as silver, arsenic, bismuth, cobalt, hexavalent chromium, mercury, antimony, and tin ions.
5. Effective removal of color and odor.
Activated Carbon Filters are widely used in water treatment engineering in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, electronics, chemicals, and industrial wastewater. They serve as pretreatment equipment in the water treatment process, preventing pollution of subsequent equipment by water contaminants. They can also be used to improve the odor and color of water.
Performance Characteristics
1. Good adsorption and filtration effects with a small footprint.
2. Easy to use and manage, low operating costs.
3. Long filter media lifespan.
6.Selection of Activated Carbon Filters
The size of the Activated Carbon Filter is determined based on water volume, and it can be made of A3 steel or stainless steel depending on the intended use. Commonly used activated carbon is granular, with a particle size ranging from 0.4 to 2.4 mm. Shapes include cylindrical, spherical, amorphous carbon, hollow spherical, and hollow cylindrical. The specific surface area ranges from 500 to 1500 m2/g of carbon, and the total
specification | Water outlet (t/h) | Activated carbon filter material | operating weight (t) | ||
story height (mm | Weight (kg) | Cushion weight (kg) | |||
DN400 | 1 | 1200 | 80 | 0.45 | |
DN500 | 2 | 126 | 0.75 | ||
DN600 | 3 | 181 | 0.89 | ||
DN800 | 5 | 1600 | 320 | 2.5 | |
DN1000 | 8 | 500 | 2.9 | ||
DN1200 | 12 | 2000 | 904 | 1046 | 4.9 |
DN1500 | 18 | 1413 | 2128 | 8.3 | |
DN1600 | 20 | 1608 | 2531 | 9.5 | |
DN1800 | 25 | 2035 | 2907 | 11.65 | |
DN2000 | 31 | 2513 | 3490 | 14.1 | |
DN2200 | 37 | 3040 | 4471 | 16.9 | |
DN2500 | 49 | 3925 | 5567 | 21.1 | |
DN2800 | 62 | 4924 | 6676 | 28.3 | |
DN3000 | 70 | 5652 | 8130 | 30.9 | |
DN3200 | 80 | 6431 | 9614 | 38.9 |
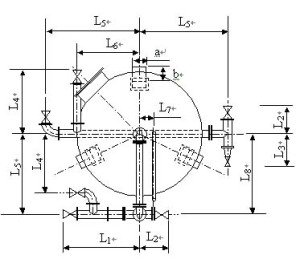
7. Activated Carbon Filter Model and Schematic Diagram
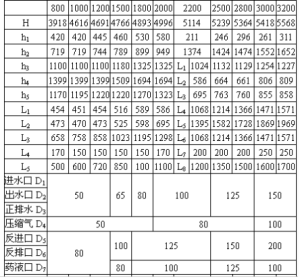
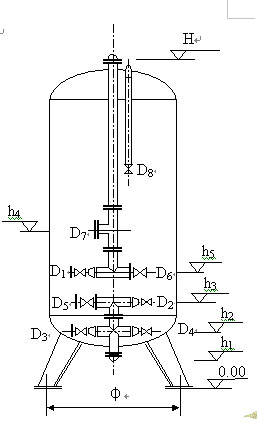
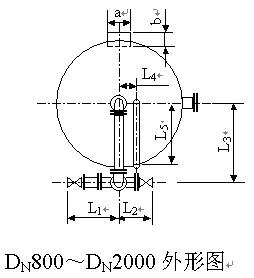
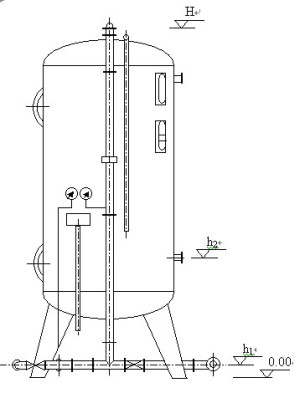
8.Common Problems and Solutions of Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon filters, as important equipment for water treatment, although powerful, may encounter some common problems in practical use. The following lists some common problems and their possible solutions:
1. **Dark water quality during initial operation**: This is usually caused by the flushing of impurities in the activated carbon filter when it is started for the first time or restarted after a long period of inactivity. It is recommended to continue running for a period of time and use it after the water quality returns to normal.
. **Activated carbon particles in the outlet water**: This may be due to damage to the internal filter screen of the filter, causing activated carbon particles to flow out with the water. The filter screen needs to be replaced at this time.
3. **Loss of activated carbon during backwashing**: This may be due to damage to the filter screen at the bottom of the filter, causing the activated carbon to be lost during the backwashing process. The filter screen needs to be replaced at this time.
4. **The water output is far below the design value**: This may be due to the internal blockage of the activated carbon filter, which causes water flow to be blocked. Backwashing should be performed to remove the blocked impurities.
5. **Water quality test results are not satisfactory**: This may be due to the saturation of the activated carbon in the activated carbon filter, which can no longer adsorb impurities in the water. The activated carbon needs to be replaced at this time.
6. **There are small particles inside the equipment**: This may be caused by the scattering of activated carbon particles during transportation or installation. The equipment can continue to run for a period of time, and the small particles can be flushed out of the equipment by the water flow.
7. **Leakage of equipment frame**: This may be caused by poor sealing of the frame or aging of the sealant. The sealant strip can be inspected and replaced or new sealant can be applied at this time.
8. **Equipment air leakage**: This may be caused by damage to the internal sealing strip of the equipment or loosening of the connections. It is necessary to inspect and replace the sealing strip or tighten the connections at this time.
9. **Large amount of water leakage from the equipment**: This may be caused by manufacturing defects in the equipment itself or damage during use. The entire equipment needs to be replaced at this time.
10. **Low face velocity of the filter**: This may be due to the saturation of the activated carbon inside the filter, which cannot continue to provide sufficient filtering area. The activated carbon needs to be replaced or the entire filter needs to be replaced at this time.
The above are some common problems and their solutions that may be encountered during the use of activated carbon filters. To ensure the normal operation and filtering effect of the equipment, it is recommended to regularly maintain and inspect the equipment, and promptly replace damaged components and saturated activated carbon.

